How To Prepare Your Business for Compliance: A Guide Beyond SOC 2
Consider this scenario: An established business, already making strides in its industry, encounters a pivotal challenge—regulatory compliance. As they expand and evolve, they face a complex landscape of legal requirements that could threaten their progress. Yet, this challenge is also an opportunity. By adopting a compliance-first strategy, not only can the business meet SOC 2 standards, including both SOC 2 Type 1 and SOC 2 Type 2, but it can also align with other critical regulations such as ISO 27001 and HIPAA. This comprehensive approach to compliance is not just about adhering to standards; it’s a foundational element for sustaining success, enhancing reputation, and securing growth.
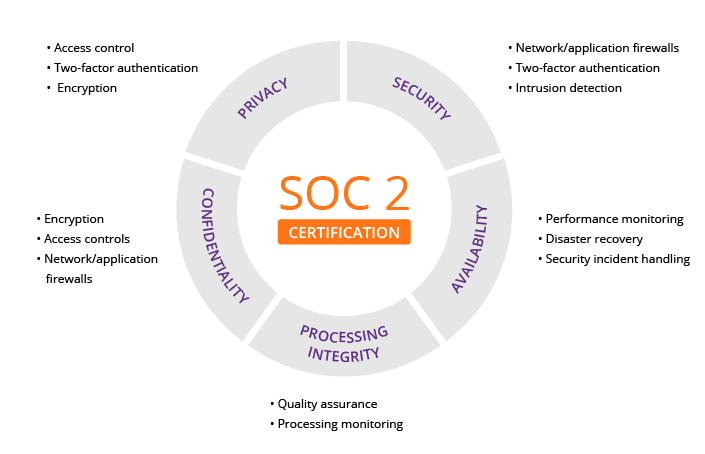
The Compliance Framework: Universal Steps for SOC 2 and Beyond
1. Research Your Compliance Needs:
Start with a comprehensive understanding of the specific compliance requirements relevant to your industry and location. Whether mandatory or optional, getting this right sets the foundation. Consulting with a compliance expert can steer you in the right direction early on.
2. Invest in the Right Technologies:
Technology is your ally in the compliance journey. Opt for solutions that not only meet your current needs but are scalable for future demands. Technologies that facilitate seamless audits and incorporate critical security features are invaluable.
3. Conduct a Risk Assessment:
Identify potential threats and vulnerabilities to devise a robust security strategy. A systematic risk assessment informs the development of targeted defenses, ensuring your security measures are both effective and efficient.
Here’s a concise breakdown of the key steps involved in conducting a security risk assessment:
- Scope Definition: Identify the boundaries of the assessment, including systems, data, and processes.
- Asset Identification: List all assets within the scope, categorizing them based on importance.
- Threat Identification: Determine potential threats to each asset.
- Vulnerability Identification: Identify weaknesses that could be exploited by the threats.
- Risk Analysis: Assess the likelihood and impact of each threat exploiting a vulnerability.
- Risk Evaluation: Compare the risks against risk criteria to prioritize them.
- Risk Treatment: Decide on how to address each risk, whether by accepting, avoiding, transferring, or mitigating it.
- Documentation and Reporting: Document the findings and recommendations for stakeholders.
- Review and Update: Regularly review and update the risk assessment to reflect changes in the environment or business.
4. Write Policies That Mitigate Identified Risks:
Draft clear, concise policies to address the risks your business faces. These policies form the backbone of your compliance strategy, guiding administrative, physical, and technical controls.
Here’s a brief rundown of typical security policies organizations often need to implement:
- Information Security Policy: Outlines how a company protects and manages confidential data.
- Access Control Policy: Defines who can access specific data and systems, and under what conditions.
- Incident Response Policy: Details the steps to be taken in the event of a security breach or incident.
- Data Retention and Destruction Policy: Specifies how long data is kept and the procedures for securely deleting it.
- Acceptable Use Policy: Describes the proper use of company resources and the internet to prevent misuse.
- Change Management Policy: Procedures for managing changes to IT systems, ensuring they don’t compromise security.
- Password Policy: Covers the creation, management, and use of passwords, specifying requirements like complexity, expiration, and storage to ensure strong authentication practices.
- Network Policy: Details guidelines for network setup, access, and use, including segmentation, protection measures, and monitoring to secure against unauthorized access and threats.
- Security Awareness and Training Policy: Establishes the requirement for regular security training for employees, detailing the frequency and content of the training to enhance the organization’s security culture.
- Incident Response Policy: Outlines the procedures for responding to security incidents, including roles and responsibilities, reporting mechanisms, and steps for containment, eradication, and recovery.
- Data Security Policy: Specifies how sensitive or critical data is handled, protected, and shared, including encryption, access controls, and data lifecycle management.
- Asset Management Policy: Defines the process for tracking and managing physical and digital assets, ensuring they are properly inventoried, used, and maintained securely.
- Remote Access Policy: Sets the rules for remote access to the organization’s network and systems, including the use of secure connections, authentication methods, and device management to mitigate risks associated with remote work.
- Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery Policy: This policy outlines the organization’s strategies for continuing operations during and recovering after a disaster or significant disruption, ensuring minimal impact on business functions.
- Email Security Policy: Specifies the rules for email use, including handling of sensitive information, attachment restrictions, and phishing scam awareness, to protect against email-based threats and ensure secure communication.
5. Implement Security Controls:
With your policies as a roadmap, implement security controls to address identified gaps. Whether you’re refining existing systems or introducing new solutions, the goal is seamless integration of security into your business operations.
6. Establish a System for Evidence Retention:
Demonstrating compliance requires tangible evidence. Develop a system to gather and retain documentation, ensuring you can substantiate your compliance efforts during audits.
7. Regular Audits and Remediation:
Compliance is not a one-time achievement but a continuous process. Regular audits help you stay aligned with evolving standards and regulations, fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
Conclusion:
Achieving and maintaining compliance is a dynamic journey that positions your business for success. By adopting a compliance-first approach, you not only safeguard your operations but also enhance your market reputation. Remember, the path to compliance, while focused here on SOC 2, is versatile—these foundational steps can guide you through any regulatory landscape. Start your journey today and turn compliance into your competitive edge.
Do you need help with your IT, compliance, or policies? Cynxt can help! We provide IT Solutions that will provide you a peace of mind. Contact Us today or call (256) 456-5858 to schedule an appointment. We are located at the Shoals Business Incubator in Florence, AL. Let us help you keep your digital life running smoothly!
Cynxt Service Areas:
We proudly serve businesses in the following areas and surrounding cities. Click here to view the full list. Remote support is also available for businesses anywhere.
North Alabama:
- Florence
- Muscle Shoals
- Russellville
- Athens
- Decatur
- Huntsville
Middle Tennessee:
- Franklin
- Columbia
- Lawrenceburg
- Pulaski
About Us:
With over 18 years of IT experience, Cynxt IT Services delivers enterprise-level solutions tailored to small and medium-sized businesses. As a trusted Managed Service Provider (MSP), we’re dedicated to supporting your growth with reliable, expert IT services and unmatched customer care.
Services:
Explore our wide range of IT Services. Learn more about how we can help with your IT needs. Not finding the service you’re looking for? Contact Us to discuss custom solutions.
- Managed IT Services
- Hourly IT Support
- Cybersecurity
- Cloud Services
- Networking
- Network Cabling
- IT Consulting





